ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting
FY 2022
5. Chapter 5: Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopmental disorders
(F01 – F99)
a. Pain disorders related to psychological factors
Assign code F45.41, for pain that is exclusively related to psychological
disorders. As indicated by the Excludes 1 note under category G89, a code from
category G89 should not be assigned with code F45.41.
Code F45.42, Pain disorders with related psychological factors, should be used
with a code from category G89, Pain, not elsewhere classified, if there is
documentation of a psychological component for a patient with acute or chronic
pain.
See Section I.C.6. Pain
b. Mental and behavioral disorders due to psychoactive substance
use
1) In Remission
Selection of codes for “in remission” for categories F10-F19, Mental and
behavioral disorders due to psychoactive substance use (categories F10-
F19 with -.11, -.21) requires the provider’s clinical judgment. The
appropriate codes for “in remission” are assigned only on the basis of
provider documentation (as defined in the Official Guidelines for Coding
and Reporting), unless otherwise instructed by the classification.
ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding andReporting
FY 2022
Page 41 of 115
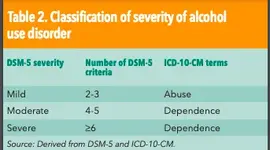
Mild substance use disorders in early or sustained remission are
classified to the appropriate codes for substance abuse in remission, and
moderate or severe substance use disorders in early or sustained
remission are classified to the appropriate codes for substance
dependence in remission.
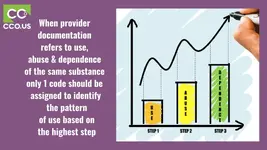
2) Psychoactive Substance Use, Abuse and Dependence
When the provider documentation refers to use, abuse and dependence of
the same substance (e.g. alcohol, opioid, cannabis, etc.), only one code
should be assigned to identify the pattern of use based on the following
hierarchy:
• If both use and abuse are documented, assign only the code for
abuse
• If both abuse and dependence are documented, assign only the code
for dependence
• If use, abuse and dependence are all documented, assign only the
code for dependence
• If both use and dependence are documented, assign only the code
for dependence.
3) Psychoactive Substance Use, Unspecified
As with all other unspecified diagnoses, the codes for unspecified
psychoactive substance use (F10.9-, F11.9-, F12.9-, F13.9-, F14.9-,
F15.9-, F16.9-, F18.9-, F19.9-) should only be assigned based on
provider documentation and when they meet the definition of a
reportable diagnosis (see Section III, Reporting Additional Diagnoses).
These codes are to be used only when the psychoactive substance use is
associated with a substance related disorder (chapter 5 disorders such
as sexual dysfunction, sleep disorder, or a mental or behavioral disorder)
or medical condition, and such a relationship is documented by the
provider.
4) Medical Conditions Due to Psychoactive Substance Use, Abuse
and Dependence
Medical conditions due to substance use, abuse, and dependence are
not classified as substance-induced disorders. Assign the diagnosis
code for the medical condition as directed by the Alphabetical Index
along with the appropriate psychoactive substance use, abuse or
dependence code. For example, for alcoholic pancreatitis due to
alcohol dependence, assign the appropriate code from subcategory
K85.2, Alcohol induced acute pancreatitis, and the appropriate code
from subcategory F10.2, such as code F10.20, Alcohol dependence,
uncomplicated. It would not be appropriate to assign code F10.288,
Alcohol dependence with other alcohol-induced disorder.
5) Blood Alcohol Level
ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding andReporting
FY 2022
Page 42 of 115
A code from category Y90, Evidence of alcohol involvement
determined by blood alcohol level, may be assigned when this
information is documented and the patient’s provider has
documented a condition classifiable to category F10, Alcohol related
disorders. The blood alcohol level does not need to be documented
by the patient’s provider in order for it to be coded.
Reporting E/M services using “Time”
• When counseling or coordination of care dominates (more than 50%) the physician/patient or family
encounter (face-to-face time in the office or other outpatient setting or floor/unit time in the hospital or nursing
facility), then time shall be considered the key or controlling factor to qualify for a particular level of E/M
services.
• This includes time spent with parties who have assumed responsibility for the care of the patient or decision
making whether or not they are family members (eg, foster parents, person acting in loco parentis, legal
guardian). The extent of counseling and/or coordination of care must be documented in the medical record.
• For coding purposes, face-to-face time for these services is defined as only that time that the physician
spends face-to-face with the patient and/or family. This includes the time in which the physician performs such
tasks as obtaining a history, performing an examination, and counseling the patient.
+ Codes are add-on codes, meaning they are reported separately in addition to the appropriate code for the service provided
Current Procedural Terminology© 2017 American Medical Association. All Rights Reserved.
• When codes are ranked in sequential typical times (such as for the office-based E/M services or consultation
codes) and the actual time is between 2 typical times, the code with the typical time closest to the actual time is
used.
• Prolonged services can only be added to codes with listed typical times such as the ones listed above. In
order to report physician or other qualified health care professional prolonged services (99354-99355) the
reporting provider must spend a minimum of 30 minutes beyond the typical time listed in the code level being
reported. When reporting outpatient prolonged services only count face-to-face time with the reporting
provider. When reporting inpatient or observation prolonged services you can count face-to-face time, as well
as unit/floor time spent on the patient’s care. However, if the reporting provider is reporting their service based
on time (ie, counseling/coordinating care dominate) and not key components, then prolonged services cannot
be reported unless the provider reaches 30 minutes beyond the listed typical time in the highest code in the set
(eg, 99205, 99226, 99223). It is important that time is clearly noted in the patient’s chart.
 www.aapc.com
www.aapc.com

 www.cco.us
www.cco.us

 www.acepnow.com
www.acepnow.com

 www.acepnow.com
www.acepnow.com
 www.acog.org
www.acog.org
FY 2022
5. Chapter 5: Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopmental disorders
(F01 – F99)
a. Pain disorders related to psychological factors
Assign code F45.41, for pain that is exclusively related to psychological
disorders. As indicated by the Excludes 1 note under category G89, a code from
category G89 should not be assigned with code F45.41.
Code F45.42, Pain disorders with related psychological factors, should be used
with a code from category G89, Pain, not elsewhere classified, if there is
documentation of a psychological component for a patient with acute or chronic
pain.
See Section I.C.6. Pain
b. Mental and behavioral disorders due to psychoactive substance
use
1) In Remission
Selection of codes for “in remission” for categories F10-F19, Mental and
behavioral disorders due to psychoactive substance use (categories F10-
F19 with -.11, -.21) requires the provider’s clinical judgment. The
appropriate codes for “in remission” are assigned only on the basis of
provider documentation (as defined in the Official Guidelines for Coding
and Reporting), unless otherwise instructed by the classification.
ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding andReporting
FY 2022
Page 41 of 115
Mild substance use disorders in early or sustained remission are
classified to the appropriate codes for substance abuse in remission, and
moderate or severe substance use disorders in early or sustained
remission are classified to the appropriate codes for substance
dependence in remission.
2) Psychoactive Substance Use, Abuse and Dependence
When the provider documentation refers to use, abuse and dependence of
the same substance (e.g. alcohol, opioid, cannabis, etc.), only one code
should be assigned to identify the pattern of use based on the following
hierarchy:
• If both use and abuse are documented, assign only the code for
abuse
• If both abuse and dependence are documented, assign only the code
for dependence
• If use, abuse and dependence are all documented, assign only the
code for dependence
• If both use and dependence are documented, assign only the code
for dependence.
3) Psychoactive Substance Use, Unspecified
As with all other unspecified diagnoses, the codes for unspecified
psychoactive substance use (F10.9-, F11.9-, F12.9-, F13.9-, F14.9-,
F15.9-, F16.9-, F18.9-, F19.9-) should only be assigned based on
provider documentation and when they meet the definition of a
reportable diagnosis (see Section III, Reporting Additional Diagnoses).
These codes are to be used only when the psychoactive substance use is
associated with a substance related disorder (chapter 5 disorders such
as sexual dysfunction, sleep disorder, or a mental or behavioral disorder)
or medical condition, and such a relationship is documented by the
provider.
4) Medical Conditions Due to Psychoactive Substance Use, Abuse
and Dependence
Medical conditions due to substance use, abuse, and dependence are
not classified as substance-induced disorders. Assign the diagnosis
code for the medical condition as directed by the Alphabetical Index
along with the appropriate psychoactive substance use, abuse or
dependence code. For example, for alcoholic pancreatitis due to
alcohol dependence, assign the appropriate code from subcategory
K85.2, Alcohol induced acute pancreatitis, and the appropriate code
from subcategory F10.2, such as code F10.20, Alcohol dependence,
uncomplicated. It would not be appropriate to assign code F10.288,
Alcohol dependence with other alcohol-induced disorder.
5) Blood Alcohol Level
ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding andReporting
FY 2022
Page 42 of 115
A code from category Y90, Evidence of alcohol involvement
determined by blood alcohol level, may be assigned when this
information is documented and the patient’s provider has
documented a condition classifiable to category F10, Alcohol related
disorders. The blood alcohol level does not need to be documented
by the patient’s provider in order for it to be coded.
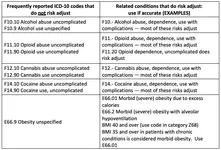
Alcohol Use, Abuse, and Dependence Codes
A code from code section F10.- would be reported for a diagnosis of alcohol use, abuse, or dependence. Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopmental Disorders (F01–F99) codes are found in Chapter 5 of ICD-10-CM. Possible ICD-10 codes linked to the counseling and office visit code as follows:- Code: F10.9-
- Description: Alcohol use, unspecified
- Code: F10.1-
- Description: Alcohol abuse
- Code: F10.2-
- Description: Alcohol dependence
- Code: Z86.59
- Description: Personal history of other mental and behavioral disorders
- Code: Z81.1
- Description: Family History of Alcohol Abuse and Dependence
- Code: Z71.41
- Description: Alcohol abuse counseling and surveillance of alcoholic (use additional code for alcohol abuse or dependence (F10.-)
- Code: 99401-99404
- Description: Preventive medicine, individual counseling
- Code: 99411-99412
- Description: Preventive medicine, group counseling
- Code: 99408
- Description: Alcohol and/or substance abuse, structured (eg, AUDIT, DAST), and brief intervention (SBI) service; 15 to 30 minutes (Do not report services of less than 15 minutes with 99408)
- Code: 99409
- Description: Alcohol and/or substance abuse, structured (eg, AUDIT, DAST), and brief intervention (SBI) service; Greater than 30 minutes (Do not report 99409 in conjunction with 99408. Use 99408 or 99409 only for initial screening and brief intervention)
- Code: 99201-99205
- Description: New patient, office, or other outpatient visit
- Code: 99211-99215
- Description: Established patient, office, or other outpatient visit

Reporting E/M services using “Time”
• When counseling or coordination of care dominates (more than 50%) the physician/patient or family
encounter (face-to-face time in the office or other outpatient setting or floor/unit time in the hospital or nursing
facility), then time shall be considered the key or controlling factor to qualify for a particular level of E/M
services.
• This includes time spent with parties who have assumed responsibility for the care of the patient or decision
making whether or not they are family members (eg, foster parents, person acting in loco parentis, legal
guardian). The extent of counseling and/or coordination of care must be documented in the medical record.
• For coding purposes, face-to-face time for these services is defined as only that time that the physician
spends face-to-face with the patient and/or family. This includes the time in which the physician performs such
tasks as obtaining a history, performing an examination, and counseling the patient.
+ Codes are add-on codes, meaning they are reported separately in addition to the appropriate code for the service provided
Current Procedural Terminology© 2017 American Medical Association. All Rights Reserved.
• When codes are ranked in sequential typical times (such as for the office-based E/M services or consultation
codes) and the actual time is between 2 typical times, the code with the typical time closest to the actual time is
used.
• Prolonged services can only be added to codes with listed typical times such as the ones listed above. In
order to report physician or other qualified health care professional prolonged services (99354-99355) the
reporting provider must spend a minimum of 30 minutes beyond the typical time listed in the code level being
reported. When reporting outpatient prolonged services only count face-to-face time with the reporting
provider. When reporting inpatient or observation prolonged services you can count face-to-face time, as well
as unit/floor time spent on the patient’s care. However, if the reporting provider is reporting their service based
on time (ie, counseling/coordinating care dominate) and not key components, then prolonged services cannot
be reported unless the provider reaches 30 minutes beyond the listed typical time in the highest code in the set
(eg, 99205, 99226, 99223). It is important that time is clearly noted in the patient’s chart.
Smoking and Alcohol Addiction: Tough Codes to Crack!
Be Ready as More Patients Seek Help By Meera Mohanakrishnan, MSc, CPC There are two codes for tobacco use cessation counseling and two codes for alcohol

Coding Alcohol and Smoking Dependence vs. Severe Use Disorder
Coding Alcohol and Smoking Dependence vs. Severe Use Disorder — DSM stands for Diagnostic and Statistical Manual and it’s of mental and behavioral disorders

Billing for Alcohol and Drug Counseling - ACEP Now
ACEP Now offers real-time clinical news, news from the American College of Emergency Physicians, and news on practice trends and health care reform for the emergency medicine physician. ACEP Now is an official publication of the American College of Emergency Physicians.

Billing, Coding Tips for Smoke Cessation Counseling in the Emergency Department - ACEP Now
ACEP Now offers real-time clinical news, news from the American College of Emergency Physicians, and news on practice trends and health care reform for the emergency medicine physician. ACEP Now is an official publication of the American College of Emergency Physicians.