Coding for Obesity
Diagnosis Coding
General
Correct coding implies that the code selection is:- The most accurate description of “what” was performed and “why” it was performed
- Supported by documentation in the medical record
- Consistent with coding conventions and guidelines
Basic Guidelines for Diagnosis Coding
- Code to the highest degree of specificity.
- Code to the highest degree of certainty.
- Link the diagnosis code to the procedure code (CPT) on the claim.
- Sequence the diagnoses, reporting the primary diagnosis first, followed by the secondary, etc.
- Code only diagnoses relevant for the current encounter.
Screening for Obesity
The ICD-10-CM diagnosis code that may be reported for obesity screening is Z13.89 (Encounter for screening for other disorder).Treatment
A code from code section E66.- would be reported for a diagnosis of obesity. Endocrine, Nutritional, and Metabolic Diseases (E00-E89) codes are found in Chapter 4 of ICD-10-CM. The dash “-” used in this document indicates that an additional character or characters are required for appropriate code selection. Possible ICD-10-CM codes to report linked to the counseling and office visit codes are as follows.Commonly Reported Codes:
- Obesity (not otherwise specified) E66.9
- Obesity, extreme or morbid E66.01
Other Obesity Codes
- Obesity due to excess calories E66.0
- Morbid (severe) obesity due to excess calories E66.01
- Other obesity due to excess calories E66.09
- Drug-induced obesity E66.1
- Morbid (severe) obesity with alveolar hypoventilation E66.2
- Overweight E66.3
- Other obesity E66.8
- Obesity, unspecified E66.9
Body Mass Index Codes
Body mass index codes are located in Chapter 21 (Factors Influencing Health Status and Contact with Health Services (Z00-Z99)) of ICD-10-CM. A code from code section Z68 would be reported for BMI values. The fourth and fifth characters of ICD-10-CM BMI codes match the BMI number until BMI reaches a value of 40.0. For example, a BMI of 30 would be reported with code Z68.30 BMI 30.0–30.9, adult. Body mass index codes would be reported in addition to the selected obesity code. Diagnosis codes reported for an obese patient with a BMI of 30 and no other indications would be E66.9 and Z68.30.Body mass index reporting for BMIs that are greater than 40 is as follows:
- Morbid obesity with BMI 40.0–44.9 adult Z68.41
- Morbid obesity with BMI 45.0–49.9 adult Z68.42
- Morbid obesity with BMI 50.0–59.9 adult Z68.43
- Morbid obesity with BMI 60.0–69.9 adult Z68.44
- Morbid obesity with BMI 70.0 and greater Z68.45
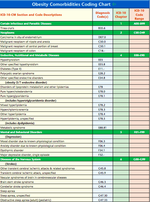
Comorbidities
When evaluating a patient for obesity and you also evaluate comorbidity conditions that you are treating or that affect your treatment, you should report the additional diagnoses codes for those conditions you evaluated that affected this specific visit, linked to the appropriate evaluation and management (CPT) code. Unlike Facility services coding, where diagnosis-related groups (DRGs) are used to identify related conditions that may affect a patient’s care and are tied to reimbursement, payment for professional services is tied to CPT procedure codes.In professional services coding, although diagnosis codes are not tied directly to provider reimbursement, they do support the medical necessity for performing specific services when linked to Coding for Obesity 2 CPT procedure codes. Reimbursement will be based on the key components (history, examination, and medical-decision-making) of the problem-oriented Evaluation and Management (E/M) service or the appropriate screening code. Alternatively, you may report a problem-oriented E/M service if more than 50% of the total time was spent counseling the patient. See the detailed discussion on time-based procedure coding below. Documentation should reflect the level and intensity of the key components or time of the total service provided. Please note that even when multiple diagnosis codes are reported, some payer edit software targets only the primary diagnosis code for the visit. As a result, you should always sequence the primary diagnosis code (ie, primary reason for the visit) for the visit, as the first linked diagnosis. Comorbidities affecting the patient’s obesity assessment, evaluation, or treatment that also are evaluated would be reported as secondary codes. (See the Obesity Comorbidities Coding Chart.)
Screening
- Encounter for screening for diabetes mellitus Z13.1
- Encounter for screening for nutritional, Z13.2 metabolic & other endocrine disorders
- Encounter for screening for nutritional disorder Z13.21
- Encounter for screening for metabolic disorder Z13.22
- Encounter for screening for lipoid disorders Z13.220
- Encounter for screening for other metabolic disorders Z13.228
- Encounter for screening for other suspected endocrine Z13.29 disorder (includes screening for thyroid disorder)
Counseling
- Dietary counseling and surveillance Z71.3
- Other specified counseling - Exercise counseling Z71.89
Procedure Coding
The most appropriate E/M code to select will depend on whether the encounter was for screening or treatment of obesity.If the encounter was for screening the patient, report a preventive medicine code from code section 99401-99412. These codes are selected according to the time spent in face-to-face counseling with the patient. Whether or not these codes will be reimbursed by the payer will vary.
Possible procedure codes are:
- Preventive medicine, individual counseling 99401-99404
- Preventive medicine, group counseling 99411-99412
Coding for Obesity 3
If the encounter was for treatment for a patient with a diagnosis of obesity, report an office or other outpatient E/M code. These codes list a “typical time” in the code descriptions. Codes with typical times listed may be reported based on time, rather than the key E/M components of; history, exam, and medical-decision-making. If the health care provider spends more that 50% of the visit counseling the patient, the E/M code may be selected based on time. Time spent providing face-to-face counseling with the patient must be documented in the medical record. The record should document total time and that either all of the encounter or more than 50% of the total time was spent counseling the patient. The patient record also must provide details on the topics discussed. Possible procedure codes to report are:- New patient, office, or other outpatient visit 99201-99205
- Established patient, office, or other outpatient visit 99211-99215
- Bariatric surgery status Z98.84
- Bariatric surgery status complicating pregnancy, O99.84-childbirth, and the puerperium
Medicare: Intensive Behavioral Therapy for Obesity
For Medicare beneficiaries with obesity, defined as a BMI greater than or equal to 30; who are competent and alert at the time that counseling is provided; and whose counseling is furnished by a qualified primary care physician or other primary care practitioner in a primary care setting, CMS will cover intensive behavioral therapy for obesity. This service is described as follows:- One face-to-face visit every week for the first month
- One face-to-face visit every other week for months 2–6
- One face-to-face visit every month for months 7–12, if the beneficiary meets the 3kg (6.6 lbs) weight loss requirement during the first 6 months as discussed below
HCPCS code G0473 (Face-to-face behavioral counseling for obesity, group (2–10), 30 minutes), may be reported if the counseling is performed in a group session.
Coding for Obesity 4
Preventive Services
Preventive Medicine Services are a type of E/M service that does not require a chief complaint.There are two types of preventive medicine services. Preventive Medicine Evaluation and Management services are reported as follows:
1. Code Description
Initial comprehensive preventive medicine evaluation and management of an individual, includingan age and gender appropriate history, examination, counseling/anticipatory guidance/risk factor
reduction interventions, and the ordering of laboratory/diagnostic procedures, new patient;
Code Age Group
- 99384 adolescent (age 12 through 17 years)
- 99385 18–39 years
- 99386 40–64 years
- 99387 65 years and older
2. Code Description
Initial comprehensive preventive medicine evaluation and management of an individual, includingan age and gender appropriate history, examination, counseling/anticipatory guidance/risk factor
reduction interventions, and the ordering of laboratory/diagnostic procedures, established
patient;
Code Age Group
- 99394 adolescent (age 12 through 17 years)
- 99395 18–39 years
- 99396 40–64 years
- 99397 65 years and older
- A comprehensive history and examination
- Counseling/anticipatory guidance/risk factor reduction interventions
- The ordering of appropriate immunizations or laboratory/diagnostic procedures, and
- Treatment of insignificant abnormalities
Medicare does not cover Preventive Services encounters as described by CPT codes 99384-99397.
Coding for Obesity 5
As indicated previously, Counseling Risk Factor Reduction and Behavioral Change Intervention services are reported with CPT codes 99401-99412. These counseling codes are used to report services for promoting health and preventing illness/injury. That is, the patient has no current symptoms or diagnosed illness.This counseling must be provided at a separate encounter from the preventive medicine services encounter described by codes 99381-99397. The counseling codes are selected according to the time spent counseling the patient. For example, a patient comes in for prepregnancy counseling, or to discuss diet and exercise, or sexual practices. The physician spends 30 minutes with the patient and reports CPT code 99402 (preventive medicine counseling; approximately 30 minutes).
If a separate and distinct problem-oriented E/M service is also provided, it may be reported separately. It is helpful to link a different/distinct diagnosis code to the problem service.
Counseling Risk Factor Reduction and Behavioral Change Intervention codes are not reported when the physician counsels an individual patient with symptoms or an established illness. In this case, a problem-oriented E/M service, from CPT code section, 99201-99215, is reported. Behavioral change interventions are for persons who have a behavior that is often considered an illness itself, such as tobacco use or substance abuse. Any E/M service reported on the same day must be distinct, and time spent providing counseling services may not be used as a basis for the E/M code selection.
For counseling groups of patients with symptoms or established illness, see code 99078 (Physician or other qualified health care professional qualified by education, training, licensure/regulation [when applicable] or educational services rendered to patients in a group setting [eg, prenatal, obesity, or diabetic instructions]).
The codes listed in the following chart are not intended to be a comprehensive list of all conditions or factors that may be evaluated when counseling or treating a patient for obesity, but rather is intended to describe the more common comorbidities.
Note: Due to ICD-10-CM specificity, many of the diagnosis code sections have multiple codes for particular conditions. As an example, diabetes has approximately 250 codes in the code section describing the various manifestations. A dash (-) in the chart indicates that additional characters are required. For the most accurate code selection, always look up codes in the code set manuals or your EMR or EHR.
Additional information on the Medicare policy for treatment of obesity may be accessed at
Search Results
BMI Chart

Coding Clinic Updates
The Coding Clinic published in the fourth quarter of 2018 specifically states that the provider must provide documentation of a clinical condition such as obesity or overweight to justify the reporting of a code for BMI.
For patients with provider documentation identifying “morbid” obesity, the code E66. 01 (morbid [severe] obesity due to excess calories) can be assigned even if the BMI is not greater than 40, per the Coding Clinic
The Official Coding Guidelines state that the BMI may be documented by other clinicians, but the associated diagnosis (such as obesity) must be documented by the patient’s provider. This issue is also supported by the Coding Clinic which goes on to state that “overweight” must meet the conditions for reporting a secondary diagnosis. Those conditions are the following:
- Clinical evaluation; or
- Therapeutic treatment; or
- Diagnostic procedures; or
- Extended the length of hospital stay; or
- Increased nursing care and/or monitoring.
Many electronic medical records (EMRs) list the BMI automatically. These codes are not intended for routine capture.
It is not appropriate to assign the diagnosis code based on BMI. This topic was discussed in the Official Coding Guidelines, Section I.A.19, “Code assignment is not based on clinical criteria used by the provider to establish the diagnosis.” (The topic was also discussed in Coding Clinic, Fourth Quarter 2016, pg. 147-149.) Code assignment is based on the physician’s documentation for the weight diagnosis.

New 2019 regulations for BMI coding
Can an ICD-10-CM body mass index (BMI) code be used as a stand-alone code?

Coding Clinic Offers Important Guidelines for Coding BMI – MedLearn Publishing
Body mass index is a heavy topic. Spring has arrived in the Northeast and people are getting back to their exercise schedules. I was thinking about this topic as I was reading Coding Clinic, Fourth Quarter 2018. One of the big topics in this issue is body mass index (BMI) (Z68.-). The Official...





