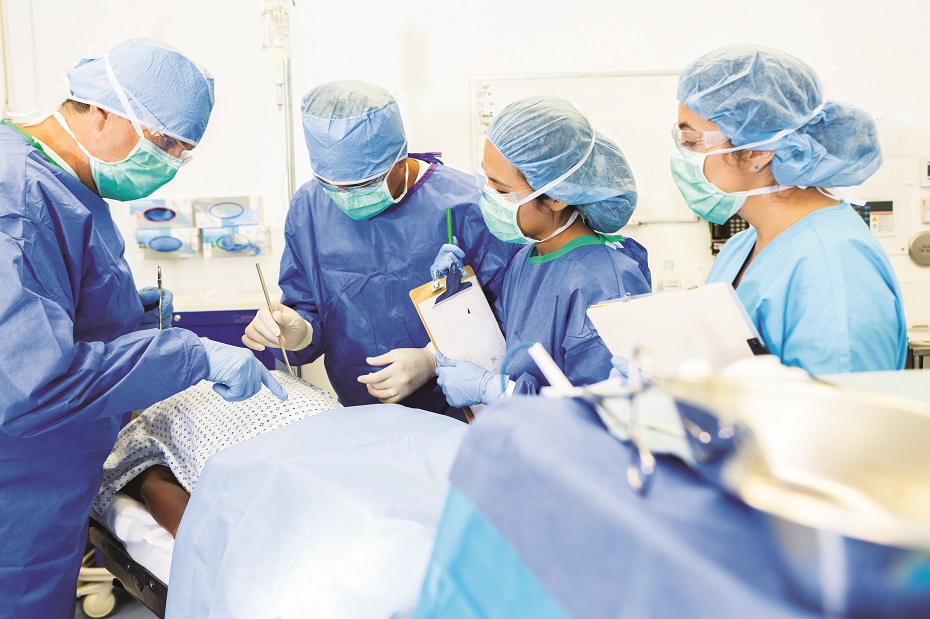
CCO Video Modifiers Made Easy:
FREE CCO TOOL:
 www.cco.us
www.cco.us
22- Increased Procedural Services
23- Unusual Anesthesia
24- Unrelated Evaluation and Management Service by the Same Physician or Other Qualified Health Care Professional During a Postoperative Period
25- Significant, Separately Identifiable Evaluation and Management Service by the Same Physician or Other Qualified Health Care Professional on the Same Day of the Procedure or Other Service
26- Professional Component
27-Multiple Outpatient Hospital E/M Encounters on the Same Date
32- Mandated Services
33- Preventative Services
47- Anesthesia by Surgeon
50- Bilateral Procedures
51- Multiple Procedures (some multiple surgical procedures must be reported WITHOUT modifier 51 identified as add on codes (appendix I)
52- Reduced Services
53- Discontinued Procedure
54- Surgical Care Only
55- Postoperative Management Only
56- Preoperative Management Only
57- Decision for Surgery
58- Staged or Related Procedure or Service by the Same Physician During the Postoperative Period
59- Distinct Procedural Service
62 -Two Surgeons
63- Procedure Performed on Infants less than 4 kg.
66- Surgical Team
73- Discontinued Outpatient Hospital/Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC) Procedure Prior to the Administration of Anesthesia
74- Discontinued Outpatient Hospital/Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC) Procedure After the Administration of Anesthesia
76 -Repeat Procedure by Same Physician or Other Qualified Health Care Professional
77- Repeat Procedure by Another Physician or Other Qualified Health Care Professional
78- Unplanned Return to the Operating Room by Same Physician or Other Qualified Health Care Professional Following Initial Procedure for a Related Procedure During the Postoperative Period
79- Unrelated Procedure or Service by the Same Physician or Other Qualified Health Care Professional During the Postoperative Period
80- Assistant Surgeon
81- Minimum Assistant Surgeon
82- Assistant Surgeon (when qualified surgeon no available)
90- Reference (Outside) Laboratory
91- Repeat Clinical Diagnostic Laboratory Test
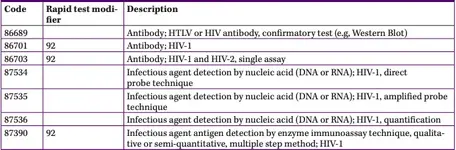
92-Alternative Laboratory Platform Testing
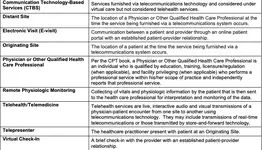
93 – Synchronous Telemedicine Service Rendered Via Telephone or Other Real-Time Interactive Audio-Only Telecommunications System
95- Synchronous Telemedicine Service Rendered Via a Real-Time Interactive Audio and Video Telecommunication System
96-Habilitative Services
97-Rehabilitative Services
99- Multiple Modifiers
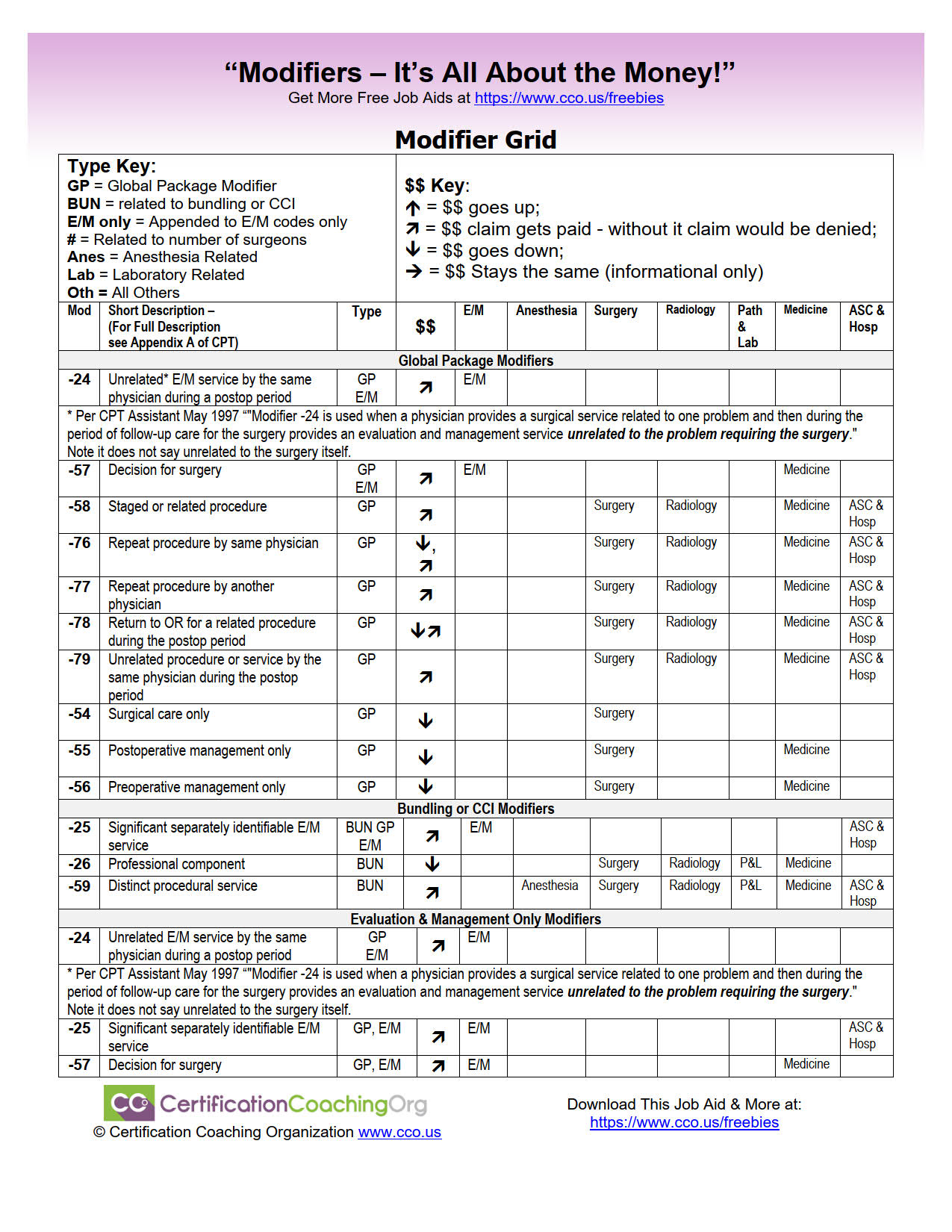
Review the proper use of each modifier.
Understand when each modifier should be applied.
FREE CCO TOOL:

CPT Modifier Decision Grid Tool
Free Job Aid: This CPT Modifier Decision Grid Tool will help you pick the correct CPT Modifiers at your medical coding job.
22- Increased Procedural Services
23- Unusual Anesthesia
24- Unrelated Evaluation and Management Service by the Same Physician or Other Qualified Health Care Professional During a Postoperative Period
25- Significant, Separately Identifiable Evaluation and Management Service by the Same Physician or Other Qualified Health Care Professional on the Same Day of the Procedure or Other Service
26- Professional Component
27-Multiple Outpatient Hospital E/M Encounters on the Same Date
32- Mandated Services
33- Preventative Services
47- Anesthesia by Surgeon
50- Bilateral Procedures
51- Multiple Procedures (some multiple surgical procedures must be reported WITHOUT modifier 51 identified as add on codes (appendix I)
52- Reduced Services
53- Discontinued Procedure
54- Surgical Care Only
55- Postoperative Management Only
56- Preoperative Management Only
57- Decision for Surgery
58- Staged or Related Procedure or Service by the Same Physician During the Postoperative Period
59- Distinct Procedural Service
62 -Two Surgeons
63- Procedure Performed on Infants less than 4 kg.
66- Surgical Team
73- Discontinued Outpatient Hospital/Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC) Procedure Prior to the Administration of Anesthesia
74- Discontinued Outpatient Hospital/Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC) Procedure After the Administration of Anesthesia
76 -Repeat Procedure by Same Physician or Other Qualified Health Care Professional
77- Repeat Procedure by Another Physician or Other Qualified Health Care Professional
78- Unplanned Return to the Operating Room by Same Physician or Other Qualified Health Care Professional Following Initial Procedure for a Related Procedure During the Postoperative Period
79- Unrelated Procedure or Service by the Same Physician or Other Qualified Health Care Professional During the Postoperative Period
80- Assistant Surgeon
81- Minimum Assistant Surgeon
82- Assistant Surgeon (when qualified surgeon no available)
90- Reference (Outside) Laboratory
91- Repeat Clinical Diagnostic Laboratory Test
92-Alternative Laboratory Platform Testing
93 – Synchronous Telemedicine Service Rendered Via Telephone or Other Real-Time Interactive Audio-Only Telecommunications System
95- Synchronous Telemedicine Service Rendered Via a Real-Time Interactive Audio and Video Telecommunication System
96-Habilitative Services
97-Rehabilitative Services
99- Multiple Modifiers
Review the proper use of each modifier.
Understand when each modifier should be applied.
- The procedure has both a professional and technical component
- Service is performed by more than 1 physician and/or in more than 1 location
- Service has been increased or reduced
- Only part of a service was performed
- An adjunctive service was performed
- Service or procedure was provided more than once
- Unusual events occurred
- Service was provided during a global period but is NOT included as part of the global reimbursement